
As 2023 draws to a close, we look at the main developments and market/technology trends during the year that shaped the e-drive components (such as e-motors, inverters) and the e-drive system integration market.
1. The increased focus on silicon carbide (SiC) devices as a way to increase EV range and enable ultra-fast charging.
An efficient inverter can increase the range and performance of an electric vehicle without significantly adding to the cost or weight of the vehicle. Owing to this improvement, automakers are increasingly moving toward wide band gap material, and SiC is one of them. SiC offers higher electric-field breakdown capability, better thermal conductivity, higher temperature operation capacity, and higher switching frequency owing to a wide electronic band gap resulting in lower switching and conduction losses compared with silicon insulated gate bipolar transistor (or Si IGBT).
Better thermal conductivity of SiC enables the inverter to dissipate heat much quicker and more efficiently. This allows the use of smaller, cost-effective cooling solutions. Furthermore, as the shift to 800V architecture is gaining traction among original equipment manufacturers, it further necessitates the use of wide band gap semiconductors such as SiC based inverters.
During the last 12 months, a series of SiC-based partnerships (mostly long-term supply agreements) took place wherein OEMs/tier 1 suppliers have partnered with SiC suppliers. The most common reason for the majority of these partnerships is to ensure a secure long-term and stable supply of SiC.
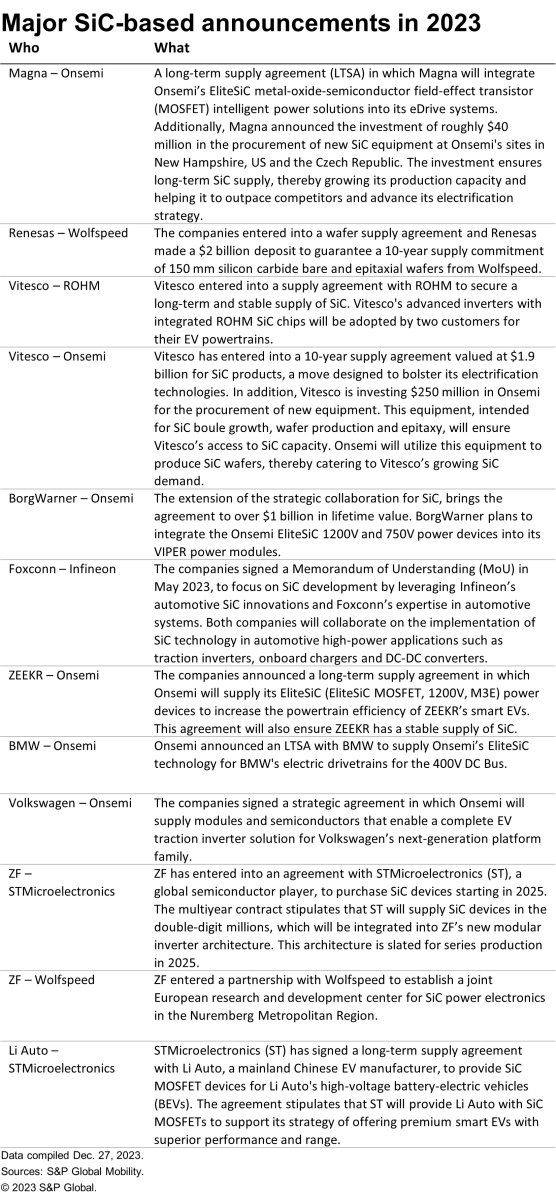
2. Increased efforts to shift from permanent magnet e-motors to magnetless (free from rare earth elements) e-motors.
Permanent magnet motors are widely used in EVs because of their higher efficiency and high-power density. The permanent magnets used in e-motors contain neodymium and dysprosium, both of which have a geographically constrained supply chain and volatile price fluctuations. Therefore, in a bid to reduce dependency on rare earth elements (REEs) — the supply chain of which is fraught with multiple challenges — OEMs and tier 1 suppliers have increased efforts to develop magnet/REE free e-motors.
During its investor day in March 2023, Tesla announced that it will design and develop a permanent magnet motor free from REEs. Recently in September 2023, ZF announced that it has developed a compact and magnet free e-motor called in-rotor inductive-excited synchronous motor (I2SM), which transmits the energy for the magnetic field via an inductive exciter inside the rotor shaft. Japan-based Proterial has developed a magnet for e-motors that need only one-fifth of terbium compared with existing magnets. The company also has plans for mass production of this new magnet and expects the start of deliveries by 2027.
3. Efforts to establish and secure REE supply chain.
S&P Global Mobility forecasts that permanent magnet e-motors will comprise approximately 80% of total eAxle motors used in EVs by 2030. As the supply chain of REEs is fraught with numerous challenges such as geopolitical issues and overdependence on mainland China, automakers are entering into strategic agreements with REE suppliers to ensure a secure and long-term supply of REEs and REE magnets.
In July 2023, Stellantis and NioCorp executed a term sheet for a rare earth offtake term agreement. This ten-year agreement aims to bolster Stellantis’ commitment to creating robust supply chains and achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2038. Concurrently, it is designed to hasten NioCorp’s journey toward the commercial production of magnetic rare earth oxides in the United States. Similarly, in January 2023, General Motors (GM) signed an agreement with Vacuumschmelze under which the latter will build a factory in North America to supply GM with REE magnets for EV e-motors for 10 years starting in 2025.
Apart from partnerships, OEMs are also investing in startups that deal with recycling of REEs or developing REE-free permanent magnets. In November 2023, both GM (through its investment arm GM Ventures) and Stellantis (through its investment arm Stellantis Ventures) participated in the funding round of Niron Magnetics that develops Clean Earth Magnets based on iron nitride that function without rare earths or other critical materials used in modern EVs. In April 2023, BMW i Ventures announced an investment in Cyclic Materials, a circular supply chain firm focused on recycling REEs, based in Canada.
Additionally, various countries are also developing regulations and policies to help establish a local and secure REE supply in a bid to reduce overdependency on mainland China for REEs.
4. Increased investments by OEMs for in-house production of e-drive components and system integration
Many OEMs are increasingly leaning toward in-house production for e-motors and system integration, as evidenced by their investments in new plants and expansion of existing production lines. This shift can be attributed to several factors, including the desire to gain a competitive edge, expedite product development and reduce costs. According to S&P Global Mobility forecasts, in-house production is the preferred strategy for e-motors and system integration, while inverters are typically outsourced. In 2023, OEMs made significant investments in the establishment and expansion of facilities for in-house production of e-motors and e-drive components.
- GM: In February 2023, GM announced its investment in its powertrain plant (which currently manufactures ICEs and transmissions for various GM car and pickup models) in Ontario to produce 400,0000 units of e-drives per annum. It also announced its plans to manufacture new Ultium electric drive units at its St. Catharines Propulsion Plant in Ontario, Canada. The plant is projected to produce over 400,000 e-drive units annually.
- Stellantis: In February 2023, Stellantis announced a $155 million investment in three Kokomo, Indiana, plants to produce new electric drive modules (EDMs). The EDMs built in the Kokomo plant will be integrated into vehicles designed on the STLA Large and STLA Frame platforms.
5. Automotive suppliers are capitalizing on the growth in EVs through strategic investments (for increased production) and mergers and acquisitions (M&As).
The swift transition to electrification is facilitating a multitude of market opportunities that OEMs and suppliers are eager to tap into. Many suppliers are investing in the construction or expansion of production facilities for the production of e-drive components and meet rising demand. Meanwhile, others are leveraging M&As to secure a strong market position, enhance their expertise and expand their product portfolio.
Some of the notable M&As of 2023 are as follows.
- Schaeffler – Vitesco: Recently, in November 2023, following Schaeffler’s voluntary tender offer to acquire Vitesco, Schaeffler and Vitesco signed a business combination agreement. This agreement will help Schaeffler to emerge as a strong supplier in the overall e-drive market with an extensive product portfolio offering e-motors and inverters. According to Schaeffler, Vitesco’s offerings will be bundled into the former’s E-mobility division with the aim of becoming an e-mobility market leader.
- Infineon – GaN System: In October 2023, Infineon completed the acquisition of GaN System to accelerate its gallium nitride (GaN) roadmap and expand its product portfolio. With the acquisition, Infineon now has 450 GaN experts and over 350 GaN patent families, expanding the company's leadership position in power semiconductors and significantly shortening time to market.
Examples of investments by suppliers in new plants/expansion include:
In July 2023, BorgWarner announced an investment in Mexico that includes a new manufacturing plant focusing on power electronics components and e-motors. ZF also announced that it will open a new e-mobility plant in Shenyang, China to produce advanced products such as eAxle drives. The first phase of the project will be launched in March 2025. Other suppliers such as Dana, Nidec, AISIN, Vitesco and Bosch have also announced significant investments for the production of e-drive components.
Conclusion
At the close of 2023, the e-drive market was marked by a focus on SiC devices for EV advancement and a shift to magnetless e-motors for sustainability. Future innovation will likely center on optimizing SiC technology and exploring alternative materials. Vertical integration by OEMs is set to continue, ensuring a streamlined production process. Collaborative efforts between automotive suppliers and cross-industry partnerships will drive competitiveness. The path forward involves sustained technological refinement, a commitment to sustainability and collective endeavors to address challenges such as motor technology advancements and infrastructure development. The e-drive market is not just adapting, but actively shaping the future of electric mobility.








